India’s pledge of zero net emissions by 2070 marks an important step in fighting climate change and creating a more sustainable future. This target aligns with the Paris Agreement’s goal of keeping global temperature increases well under 2 degrees Celsius (ideally 1.5 degrees Celsius) relative to pre-industrial levels. According to the UN Environment Program’s Emissions Gap Report 2022, India’s per capita emissions are relatively low at 2.4 tons of CO2 equivalent, as opposed to the global average of 6.3 tons.
Reaching these ambitious net zero targets requires strategic prioritization and concerted efforts across many sectors, which we will discuss here in this blog post. We will highlight which key areas should be prioritized to facilitate India’s move toward achieving Net-Zero Goals & Targets.
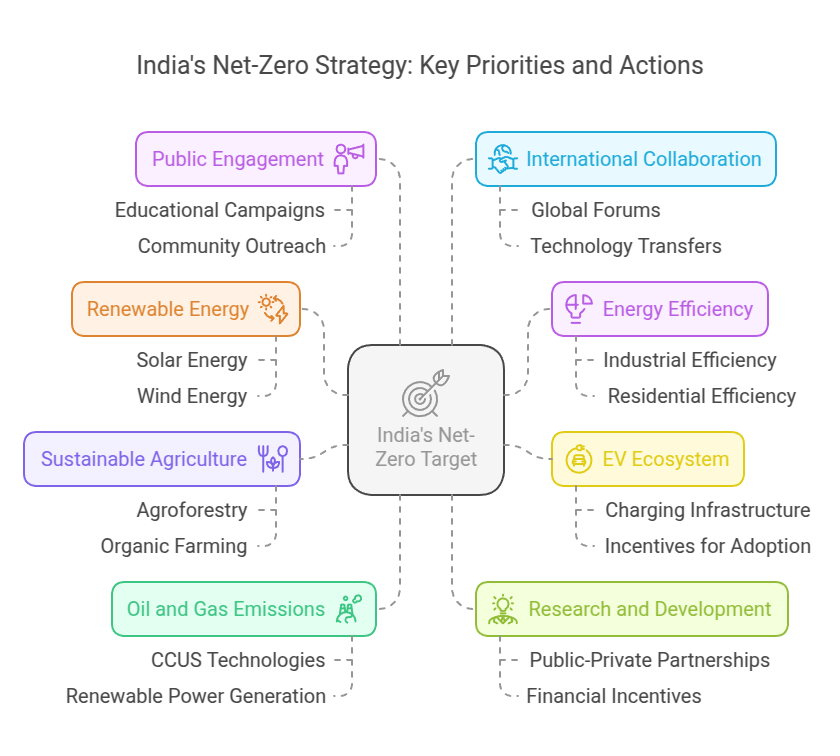
Top Priorities of India’s net-zero target
Accelerating India’s Transition to Renewable Energy
India’s heavy reliance on solar energy fossil fuels is a significant contributor to its carbon footprint. It is recorded India installed 9.7 GW of large-scale solar capacity during Q1 2024, including 1.8 GW from open access solar projects – representing a 524% QoQ increase and nearly 534% YoY rise. Such national efforts in this regard should prioritize the rapid deployment of renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower, such transitions may be supported through policy initiatives, financial incentives, or technological breakthroughs.
Encouraging rooftop solar panel adoption in urban areas can significantly lower the demand for grid electricity generated from nonrenewable sources and help meet rising energy demands while decreasing carbon emissions. It is recorded solar energy accounts for 18.6% of India’s installed power capacity and 43% of renewable energy capacity.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency across Sectors
Improving energy efficiency is a low-hanging fruit that can lead to immediate and significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. Prioritizing energy efficiency measures across industrial, commercial, and residential sectors must be given top priority as an area for improvement.
Implementing energy-efficient technologies, optimizing processes, and adopting best practices are proven strategies for cutting down energy consumption and associated emissions in industrial settings. Commercial and residential areas may experience similar savings through adopting energy-saving appliances, retrofitting buildings for better insulation, or adopting intelligent energy management systems, all contributing significantly towards cost reductions and savings in energy usage.
Building an EV Ecosystem
India’s transportation sector is one of its primary sources of carbon emissions. Transitioning to electric vehicles (EVs) could play an instrumental role in mitigating emissions while simultaneously alleviating urban air pollution issues and dependence on imported fossil fuels.
Prioritizing the establishment of an effective EV ecosystem should be a top priority, including investing in charging infrastructure, incentivizing production and adoption, and supporting research and development of advanced battery technologies. Furthermore, according to the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) India Energy Outlook 2021, India’s energy demand is projected to increase by nearly 50% by 2040 due to urbanization, industrialization, and rising living standards.
Promoting Sustainable Agriculture and Forestry Practices
India’s agricultural and forestry industries contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions through deforestation, livestock management practices, agricultural practices, and deforestation. Prioritizing more environmentally-friendly practices on net zero, sustainability can not only reduce emissions but also enhance food security and biodiversity conservation.
Encouraging Agroforestry, Precision Agriculture, and Organic Farming techniques can reduce emissions while simultaneously improving soil health by decreasing synthetic fertilizer use and pesticide emissions.
Reduce emissions from oil and gas upstream and downstream operations
There is much debate as to the best approach for combating fraudsters who may use counterfeit bills or fake IDs. For this reason, many criminals resort to using stolen identities in order to commit acts of crime such as fraudulence. As domestic fuel demand has steadily increased, the government has steadily upgraded its hydrocarbon policies in response to increased exploration, production, and distribution, including encouraging carbon-friendly technologies in these areas.
Indian upstream operators could proactively invest in on-site renewable-power generation and increase the adoption of technologies that reduce flaring and emissions, such as CCUS, for a cleaner future over the coming decades.
Investment in Research and Development (R&D)
Reaching net zero carbon emissions will require significant technological advances across many fields. Prioritizing investments in R&D will enable cutting-edge innovations to address climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies, driving innovation forward while creating cutting-edge solutions.
Encouraging public-private partnerships, establishing dedicated research centers, and offering financial incentives for innovative projects can facilitate the creation of technologies such as carbon capture and storage systems, advanced materials for energy storage purposes, sustainable manufacturing processes, and more.
Fostering Public Awareness and Engagement
Achieving net-zero carbon dioxide emissions requires more than technological or governmental solutions alone; it calls for widespread public engagement as well. Prioritizing educational campaigns, community outreach programs, and grassroots initiatives can empower individuals and communities alike to make informed choices and adopt sustainable lifestyles.
To foster a sense of collective responsibility and facilitate behavioral changes necessary for reaching net-zero emissions, encourage energy conservation practices, support recycling efforts and waste reduction strategies, and increase awareness about climate change impacts.
Strengthening International Collaboration
Climate change is a global challenge that transcends national borders. Prioritizing international collaboration and knowledge sharing to speed progress toward net-zero emissions is vital. India should participate actively in global forums, contribute to international research initiatives, collaborate on best practice development with other nations, and collaborate on developing.
Engaging in joint ventures, technology transfers, and capacity-building initiatives can help bridge the gap between developed and developing nations and ensure an equitable transition towards a sustainable future.
Bottom Line
India’s road ahead toward meeting its net-zero commitment is multifaceted and will require concerted efforts across multiple sectors. India faces an undoubtedly difficult path, yet with unwavering dedication, strategic planning and collective action it can create an enabling environment that blends economic development with environmental preservation. Now is the time to seize opportunities that present themselves so India can lead as an example of sustainable development while leaving a lasting legacy for humanity and Earth itself.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is India’s net-zero target?
India has pledged to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070, aligning with global climate goals to limit temperature rise under 2°C. -
How will renewable energy help India reach net-zero?
Expanding solar, wind, and hydropower will reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lowering emissions while ensuring sustainable energy production. -
What role do electric vehicles (EVs) play in net-zero efforts?
Transitioning to EVs reduces carbon emissions from transportation, improves air quality, and decreases dependence on imported fossil fuels. -
How can sustainable agriculture contribute to net-zero?
Practices like agroforestry, precision farming, and organic cultivation reduce emissions, enhance soil health, and promote biodiversity conservation. -
Why is international collaboration important for India’s net-zero goal?
Global partnerships enable technology transfer, joint research, and financial support, accelerating India’s transition to a low-carbon economy.
Share:
Explore More
Keep up-to-date with the most trending news stories that are shaping the world today.







