Climate change has emerged as an urgent global threat in recent decades, necessitating widespread action from every sector of society. One approach that may provide solutions is net zero emissions: “Net zero emissions” have gained prominence as an essential measure to combating climate change. By striking a balance between greenhouse gases (GHGs) released into the atmosphere and those removed or offset, we can create an era in which human potential flourishes alongside an Earth free from harm. In this article, we’ll look at its advantages for businesses as a strategy to save the planet while cutting costs and increasing market competitiveness.
What is Net Zero Emissions?
Net zero refers to an environment in which emissions of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere are balanced out with removals equaling them – thus leading to net emissions of zero overall. This approach relies on reducing emissions to the extent possible while offsetting any remaining ones with both natural solutions (trees and forests, carbon sequestration, afforestation, and reforestation), as well as technological solutions (direct air capture, carbon capture and storage (CCS), electrochemical devices). Reaching net zero carbon dioxide emissions goals is paramount to combating climate change by significantly lessening human impact on nature.
Top Priorities for India’s Net-Zero Target
As India embarks on its path toward achieving net zero emissions by 2050: An energy sector blueprint, multiple priority issues span across various sectors and necessitate a coordinated and comprehensive approach:
Renewable Energy Dominance: Accelerating India’s deployment of renewable energy options especially solar and wind power should be a top priority. Given India’s massive potential for renewable generation, policies should focus on streamlining operations, incentivizing private investment, and developing robust transmission and storage infrastructure that facilitates large-scale renewable integration into its energy mix.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation: Implementing stringent energy efficiency measures across all sectors is integral to lowering demand and emissions, such as using more efficient technologies in buildings, transportation, and industries, and awareness campaigns with incentive programs to encourage behavioural changes that reduce energy demand and associated emissions. This may include adopting energy-saving technologies in buildings, transportation, and industries, as well as encouraging behavioural modifications through awareness campaigns or incentive programs.
Electric Mobility and Green Hydrogen: Prioritizing the establishment of an effective electric vehicle ecosystem and encouraging its adoption can greatly reduce emissions from transportation and industrial sectors. Incentives for adoption, charging infrastructure development, and production/storage technologies are key areas to focus on.
Sustainable Urbanization: With rapid urbanization occurring across India, sustainable planning and development must take precedence in urban planning efforts. This includes providing public transport options, adopting green building codes, and incorporating renewable energy sources into urban infrastructure. Furthermore, effective waste management and urban greening efforts may contribute towards a low carbon goal and improved air quality.
Afforestation and Ecosystem Restoration: Enhancing carbon sinks through large-scale afforestation and ecosystem restoration initiatives is crucial for offsetting emissions, supporting sustainable land management practices, and simultaneously protecting existing forests and biodiversity.
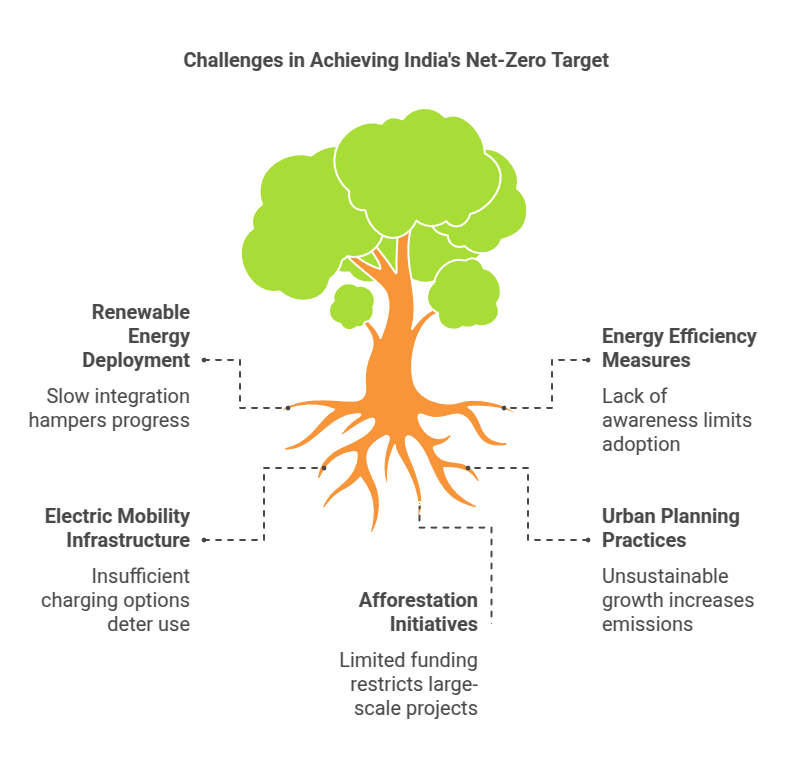
Challenges in India’s Journey to Net-Zero Emissions
While global consensus acknowledges the urgency of reaching net zero emissions, many nations worldwide still face considerable difficulties in accomplishing this ambitious goal. These primary National challenges to achieve net zero emissions span economic, technological, and societal domains and necessitate coordinated efforts and creative solutions in order to succeed in realizing it.
Economic Transition Challenges
Transitioning to a low-carbon economy requires significant investments in clean energy infrastructure, technology development, and workforce retraining. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), reaching net zero emissions by 2050 would require an annual global investment of $4 trillion globally in clean energy technologies and efficiency measures.
Technological Barriers: Certain sectors, such as aviation, shipping, and heavy industry, do not yet have low-carbon solutions readily available or require significant technological breakthroughs. IRENA estimates that over 60% of today’s emissions come from sectors in which low-carbon solutions do not yet exist or require major technological breakthroughs.
Energy Security Concerns: Many nations remain highly reliant on fossil fuels for energy production, raising concerns over security and affordability during this transition period. According to BP’s 2022 Statistical Review of World Energy report, fossil fuels accounted for 82% of primary energy consumption worldwide.
Public Acceptance and Behavior Change: Reaching net zero emissions requires lifestyle adjustments and behavioural shifts from consumers. A study published in Nature Climate Change discovered that public acceptance and willingness to change behaviour were both key indicators of policy success for zero emissions policies.
International Cooperation and Climate Finance: Developing nations may lack the financial resources and technological know-how needed to transition towards net zero emissions. According to estimates from the UN Environment Programme (UNEP), developing nations require annual investments between $1.6 and $3.8 trillion for their climate mitigation and adaptation needs.
Nations can overcome their environmental challenges through effective policymaking, international cooperation, and innovative solutions that address them effectively.
How India Is Planning to Reach Net Zero Emissions by 2050
To realize our ambitious goal of net zero emissions by 2050, a comprehensive transformation of the energy sector must occur. Here’s a Net Zero blueprint for 2050 outlining key strategies:
Accelerated Renewable Energy Deployment: At the heart of any net-zero energy system lies the rapid expansion of renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower – from solar to wind to hydro – including streamlining permitting processes, incentivizing private investments, and creating robust transmission and storage infrastructure.
Phasing Out Fossil Fuels: A gradual transition away from fossil-fuel-based power generation is critical. Achieving this transition requires clear timelines, workforce retraining programs, and support programs for affected communities.
Energy Efficiency and Demand Management: Implementing stringent energy efficiency measures across all sectors – buildings, transportation, and industry – can significantly decrease energy use and associated emissions. Technologies such as innovative smart grid technologies, demand response programs, and energy-saving appliances play a critical role.
Electrification and Hydrogen: Promoting widespread electrification of end-use sectors like transportation and heating combined with green hydrogen production can decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors while offering long-term energy storage solutions.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS): While not a silver bullet for climate action, carbon capture, and storage technologies can play a complementary role in mitigating emissions from remaining fossil fuel-based activities and industrial processes – providing a transitional solution until full decarbonization can be reached.
Sustainable Bioenergy: Exploiting sustainable bioenergy sources such as advanced biofuels and biomass can add variety to our energy mix while ensuring proper land management and mitigating any adverse environmental impacts.
Nuclear Power: Dependent upon local conditions and public perception, nuclear power may play an integral role in providing low-carbon baseload electricity, though there may be challenges related to waste management and safety that must be resolved
Achieving net zero carbon goals is an ambitious yet essential goal for securing a sustainable and prosperous future. By prioritizing renewable energy sources, energy efficiency measures, and technological innovations and addressing economic, social, and international cooperation challenges, nations can pave the way towards an inspiring net zero world.
Conclusion
Journeying towards net zero emissions is a collective endeavour, transcending borders and generations, and Hartek Group takes pride in achieving the same. Hartek Group has surpassed 7 GW of solar grid connectivity, enhancing its reputation as a leading EPC company known for delivering high-quality, timely projects and supporting India’s clean energy growth through smart grid infrastructure. The company has recently secured the 22 MW floating solar project with SJVN and is progressing towards its target of 10,000 crore sales by 2030, significantly contributing to India’s clean energy future.
To reach the goal of zero emissions, it is necessary to shift mindsets, welcome change, and remain dedicated to protecting our environment for future generations. By unlocking our potential through this transformative pursuit, we have the power to shape a future where human progress coexists peacefully with a thriving ecosystem, prosperity is interwoven with sustainability, and actions taken today pave the way for an improved tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is Net Zero and why is it important?
Net Zero means balancing greenhouse gas emissions with removals to combat climate change, ensuring a sustainable future with reduced carbon footprints. -
What are the key challenges India faces in achieving Net Zero?
Challenges include high investment needs, technological gaps, fossil fuel dependence, behavioral shifts, and the need for global climate finance. -
How is India working towards its Net Zero target by 2050?
India is focusing on renewable energy expansion, electric mobility, energy efficiency, carbon capture, and phasing out fossil fuels to meet its target. -
What role does renewable energy play in India’s Net Zero plan?
Solar, wind, and hydropower are central to India’s strategy, reducing dependency on fossil fuels and ensuring a cleaner, sustainable energy mix. -
How can businesses contribute to India’s Net Zero goal?
Businesses can invest in energy-efficient technologies, adopt sustainable practices, transition to clean energy, and support carbon offset initiatives.
Share:
Explore More
Keep up-to-date with the most trending news stories that are shaping the world today.