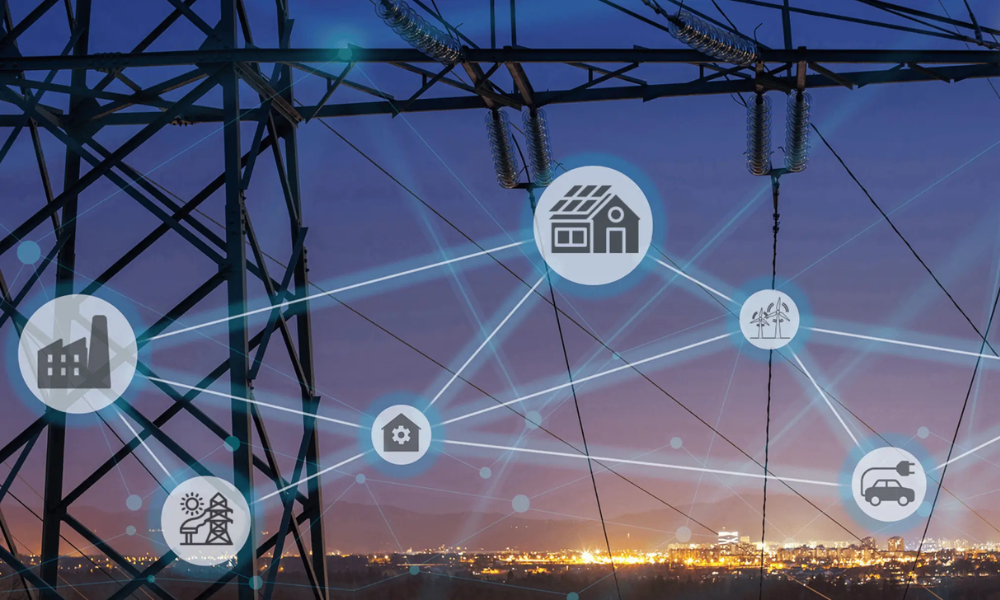
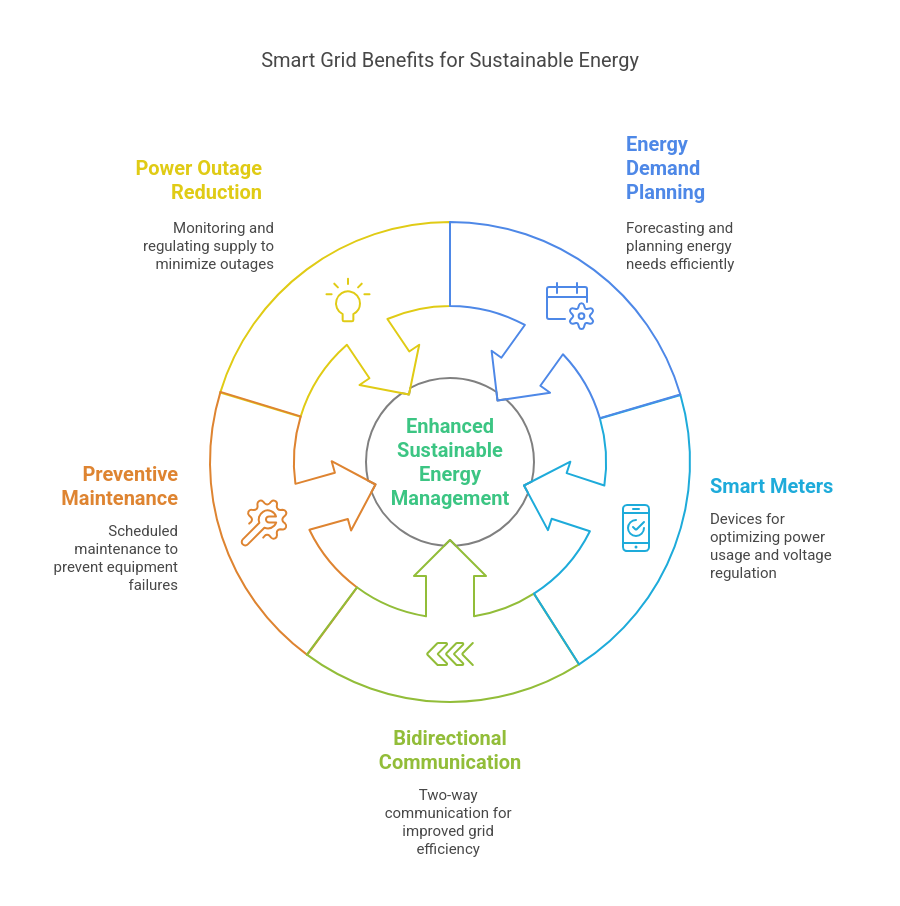
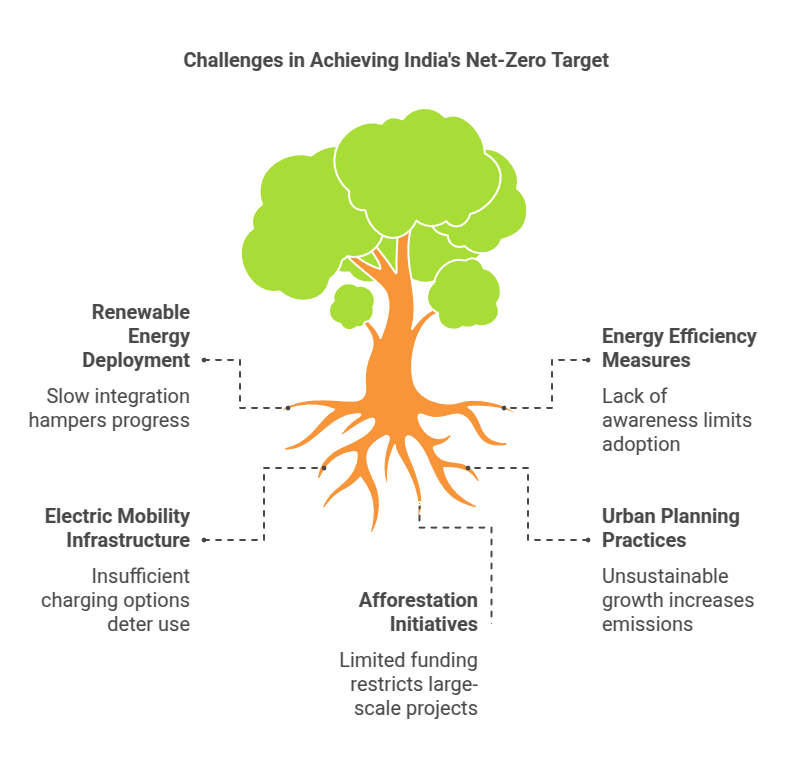
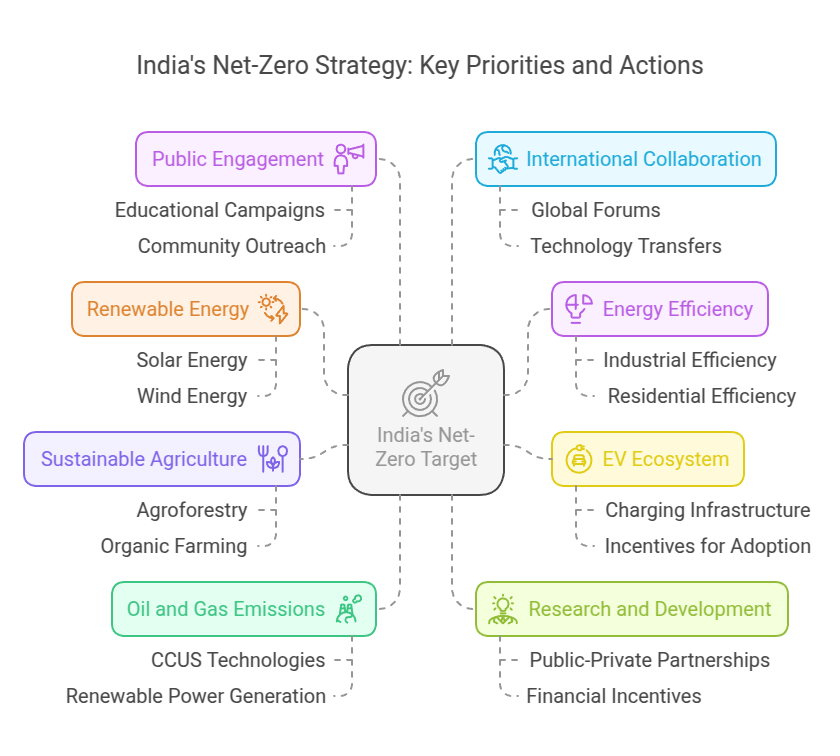
The energy consumption landscape is ever-evolving. India is taking centre stage in embracing renewable energy for sustainable development. The pressing global concern of climate change has propelled the importance of renewable sources. This makes them a pivotal force in shaping the nation’s future.
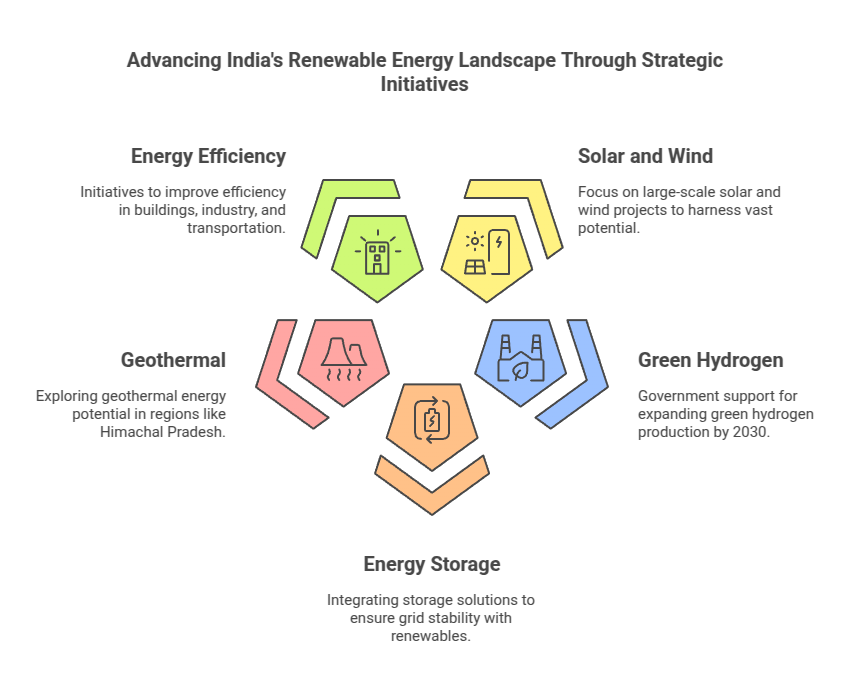
Let us look into the significance of solar, green ammonia, and hydropower in revolutionising India’s renewable energy scene. We will also spotlight the impactful contributions made by the Hartek Group.
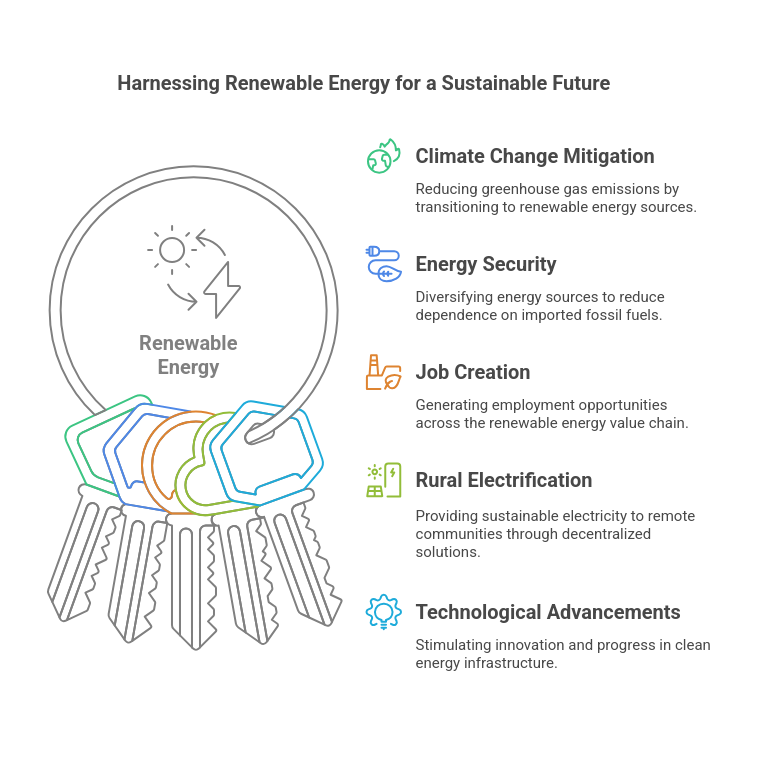
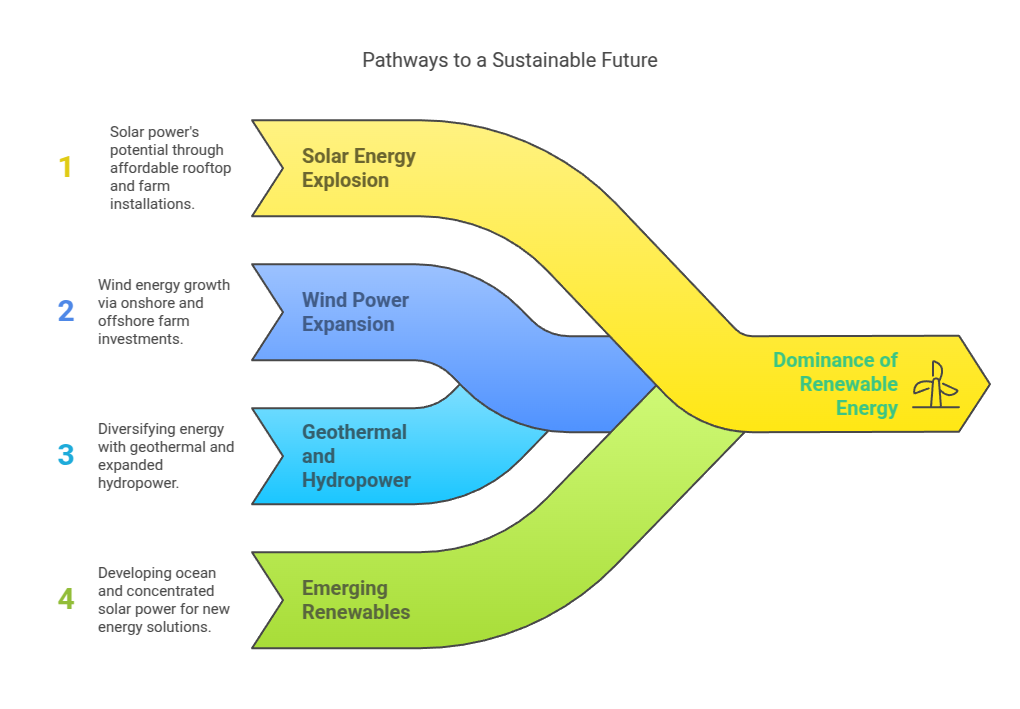
Importance of Renewable Energy
Navigating Climate Change: The adoption of renewable energy sources is a crucial step in mitigating the impacts of climate change. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, India can contribute to global efforts aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions.
Energy Security: Diversifying the energy mix with renewables enhances energy security. By tapping into abundant and indigenous sources like sunlight, wind, and water, India can reduce its dependence on imported fossil fuels. This strengthens its energy resilience.
Job Creation: The renewable energy sector has the potential to create a significant number of jobs. From manufacturing solar panels to constructing and maintaining power plants, the entire value chain offers employment opportunities. This fosters economic growth.
Rural Electrification: Renewable energy can play a pivotal role in electrifying rural areas. This is especially in the form of decentralized solar power. Off-grid solar solutions provide a sustainable and cost-effective means of bringing electricity to remote communities. This improves living standards and fosters development.
Technological Advancements: Investing in sustainable energy for industry stimulates innovation and technological advancements. As India continues to develop its clean energy infrastructure, there is a ripple effect of innovation that extends beyond the energy sector. This is influencing various industries.
Cost Competitiveness: The cost of renewable energy technologies, especially solar power, has witnessed a significant decline in recent years. This cost competitiveness makes renewable energy an attractive option. This is not just from an environmental standpoint but also from an economic perspective.
Reducing Air Pollution: Traditional forms of energy generation adversely affecting public health. These include coal-fired power plants, which contribute to air pollution. Shifting to cleaner renewable sources helps in reducing air pollutants. This leads to improved air quality and overall well-being.
Sustainable Development Goals: Embracing renewable energy aligns with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). From clean energy (SDG 7) to climate action (SDG 13) and partnerships for the goals (SDG 17), sustainable energy plays a pivotal role in achieving a sustainable and inclusive future.
Hartek Group’s Impactful Contributions
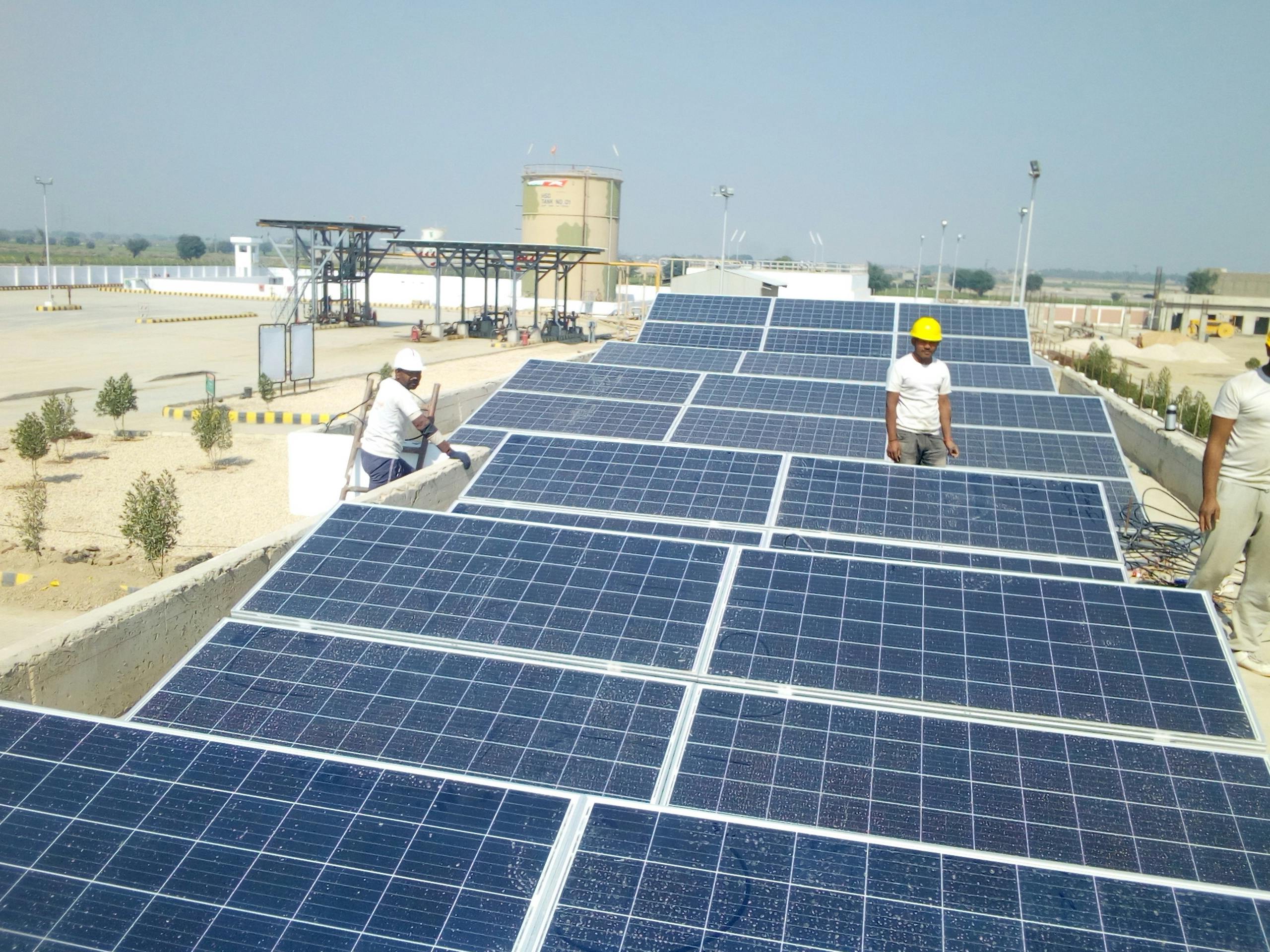
The Hartek Group has been at the forefront of driving change in India’s energy landscape. We are focused on renewable energy solutions. The group has played a pivotal role in implementing solar power projects. This contributes significantly to the country’s clean energy goals.
The Hartek Group adopts an integrated approach to renewable energy. We have encompassed design, engineering, procurement, and construction. This holistic strategy ensures the seamless execution of projects, from conceptualisation to completion.
Beyond business, the Hartek Group is committed to sustainability. By actively participating in initiatives that promote green energy and environmental conservation, the group demonstrates its dedication to creating a cleaner and greener India.
Conclusion
The importance of renewable energy for India’s sustainable development cannot be overstated. The dynamic trio of solar power, green ammonia, and hydropower is reshaping the nation’s energy landscape. They offer cleaner, more resilient, and economically viable alternatives.
The contributions of industry leaders like the Hartek Group further propel India towards a greener and more sustainable future. As the nation continues on this transformative journey, the adoption of renewable energy stands as a beacon of hope. This paves the way for a brighter, cleaner, and more sustainable tomorrow.
FAQ’s:-
1. Why is renewable energy important for India?
Renewable energy reduces carbon emissions, enhances energy security, and promotes economic growth through job creation and innovation.
2. What are the key renewable energy sources in India?
Solar power, green ammonia, and hydropower are among the top renewable energy sources revolutionizing India’s energy sector.
3. How does renewable energy support rural electrification?
Off-grid solar solutions bring cost-effective and sustainable electricity to remote communities, improving living standards and development.
4. What role does the Hartek Group play in renewable energy?
The Hartek Group leads in renewable energy solutions, executing solar power projects and promoting sustainable energy development in India.
5. How does renewable energy help in reducing air pollution?
By replacing fossil fuels, renewable energy cuts harmful emissions from coal-fired plants, improving air quality and public health.