Driven by global sustainability efforts, legislative changes, and technological developments, the power generating environment is undergoing a fundamental transition. As 2024 approaches, a number of new developments have the potential to completely transform the power generation in India by providing creative ways to both meet the rising need for energy and lessen its negative effects on the environment.
We will explore the most recent developments in the power generation industry, emphasising the innovations in technology and changes in strategy that will shape the future.
Note!
In the latest update, on May 30, 2024, India’s power demand reached a new peak of 250 GW. This record indicates rapid growth in energy consumption, spurred by weather-related causes and an increase in both industrial and residential demand.
Renewable Energy Dominance
Renewable energy is becoming an increasingly important source of power around the world. In 2024, we expect solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources to grow rapidly. Internationally, nations are setting aggressive objectives to increase their renewable energy sources, spurred by the need to combat climate change and reduce dependence on nonrenewable energy sources.
One notable trend is the rise of utility-scale solar projects. Advances in photovoltaic technology and significant cost reductions have made solar power more accessible and economically viable. Additionally, floating solar installations are emerging as a game-changer. These systems, which are installed on bodies of water, offer a unique solution to land scarcity and provide added benefits such as reduced water evaporation and improved panel efficiency due to cooler temperatures.
Hartek Group, India’s leading EPC company, has been at the forefront of this renewable energy revolution. With its Power System business unit executing over 400 extra high voltage and high voltage substation projects, Hartek has connected over 7GW of solar power to the grid, contributing significantly to India’s renewable energy capacity.
Energy Storage Solutions
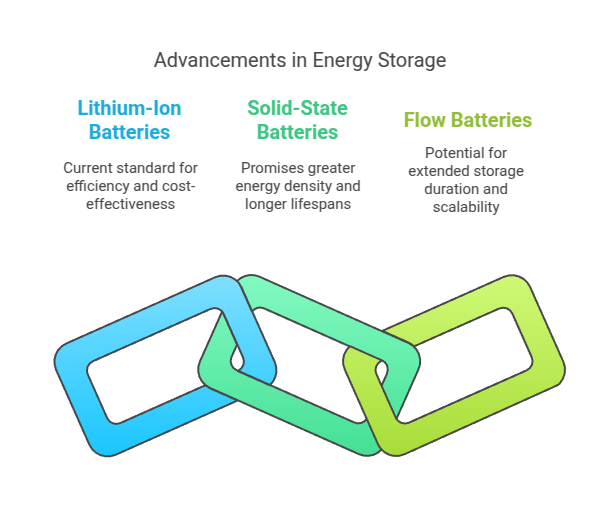
The integration of energy storage systems is another pivotal trend in 2024. As the share of intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind increases, the need for reliable energy storage solutions becomes crucial to ensure grid stability and resilience. Battery storage technology has seen remarkable advancements, with lithium-ion batteries becoming more efficient and cost-effective.
Moreover, new technologies such as solid-state batteries and flow batteries are on the horizon, promising even greater energy density and longer lifespans. These innovations are set to enhance the capability of storage systems to support renewable energy integration, enabling utilities to store excess energy during peak production periods and release it during high demand.
Decentralised Power Generation
Decentralised power generation, also known as distributed generation, is gaining traction as a key trend in 2024. This approach involves generating electricity closer to the point of consumption, reducing transmission losses and improving energy efficiency. Rooftop solar installations, microgrids, and small-scale wind turbines are prime examples of decentralised power generation.
Smart Grids and Digitalisation
The evolution of is revolutionising the power distribution sector. Smart grids leverage advanced communication and automation technologies to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and sustainable development. These systems enable real-time monitoring, fault detection, and demand response management, ensuring optimal performance and minimal downtime.
Digitalisation plays a crucial role in the development of smart grids. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics allows utilities to collect and analyse vast amounts of data. This data-driven approach facilitates predictive maintenance, reduces operational costs, and improves customer service by providing real-time insights into energy consumption patterns.
Hydrogen as an Energy Carrier
Hydrogen is emerging as a versatile energy carrier with the potential to decarbonise various sectors, including power generation, transportation, and industry. Green hydrogen, produced through electrolysis using renewable energy, is gaining attention as a clean and sustainable fuel. In 2024, significant investments are being made in hydrogen production, storage, and distribution infrastructure.
Companies are exploring hydrogen fuel cells for power generation in India, with abundant renewable energy resources. Hydrogen can be stored and transported easily, making it a viable option for balancing supply and demand in renewable energy systems. The development of hydrogen-powered turbines and hybrid systems is also underway, promising a new era of clean and efficient power generation.
Advanced Nuclear Technologies
Nuclear power remains a critical component of the global energy mix, providing a reliable and low-carbon source of electricity. In 2024, advanced nuclear technologies, such as small modular reactors (SMRs) and thorium reactors, are gaining traction. These technologies offer enhanced safety features, reduced waste generation, and greater flexibility compared to traditional nuclear reactors.
SMRs, in particular, are seen as a game-changer for the nuclear industry. Their modular design allows for easier deployment, scalability, and cost reductions. As countries seek to diversify their energy portfolios and achieve net-zero emissions, advanced nuclear technologies are poised to play a significant role in the transition to a sustainable energy future.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the power generation sector by optimising operations, enhancing efficiency, and reducing costs. AI algorithms are being employed to predict equipment failures, optimise energy dispatch, and manage energy storage systems. Machine learning models can analyse historical data to forecast energy demand and generation patterns, enabling utilities to make informed decisions.
AI is also driving innovations in renewable energy forecasting. Accurate predictions of solar and wind power generation can help grid operators balance supply and demand more effectively, reducing reliance on backup power sources. The integration of AI into energy management systems is revolutionising how we generate, distribute, and consume electricity.
Conclusion
The power generation in India is at the cusp of a transformative era, driven by technological advancements and a global commitment to sustainability. The trends emerging in 2024, from renewable energy dominance and advanced energy storage solutions to smart grids and hydrogen technologies, are reshaping the way we produce and consume electricity.
By embracing emerging ideas and creating strategic alliances, the power generation industry can help to create a more sustainable, resilient, and efficient energy sector.