With the rise of global warming, many countries are adopting renewable energy solutions. India is one of them. The country’s development is expected to embrace distributed energy systems to build a sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure. It is becoming an important cog in India’s energy machinery by allowing decentralized, efficient, and sustainable power generation. With its innovative national policies and targeted government schemes, India is making major strides towards the transparent integration of distributed energy into the national energy ecosystem.
This blog explores how India is advancing its energy sector and the growing adoption of distributed energy system in India.
What Is Distributed Energy and Why Is It Important for India?
Electricity is produced locally by small-scale sources in a distributed energy system. Consider energy sources like solar, wind, and biomass that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main electrical grid. These solutions increase grid resilience, reduce transmission losses, and improve energy efficiency.
With rapid economic growth and rising demand for electricity, conventional power systems are proving unable to keep up. Hence, it is the distributed energy system in India that comes into play. They provide flexibility, reducing dependence on fossil fuels, and helping the country achieve its sustainable goals.
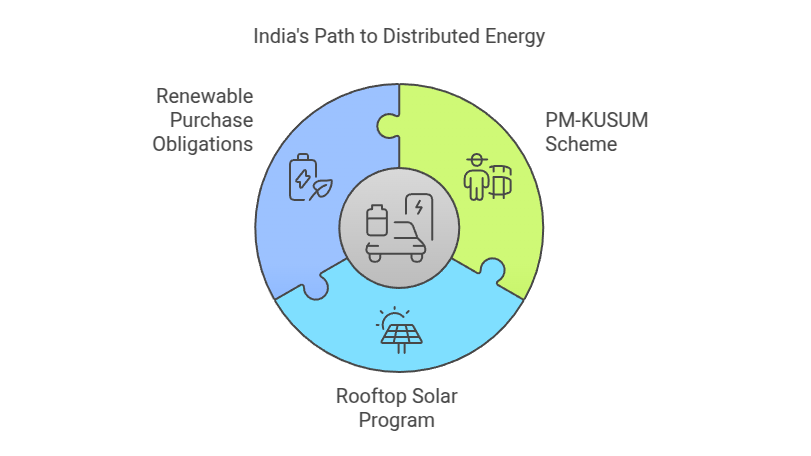
Key National Policies Supporting Distributed Energy
Several policies are paving the way for the growth of the distributed energy system in India.
1. PM-KUSUM Scheme: Empowering Rural Areas
The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM) scheme represents one of India’s largest initiatives to promote distributed energy systems.
Key benefits of the PM-KUSUM scheme include:
- Providing solar energy options to farmers.
- Lowering irrigation’s reliance on fossil fuels.
- Improving the distribution of electricity in isolated locations through the decentralization of energy production.
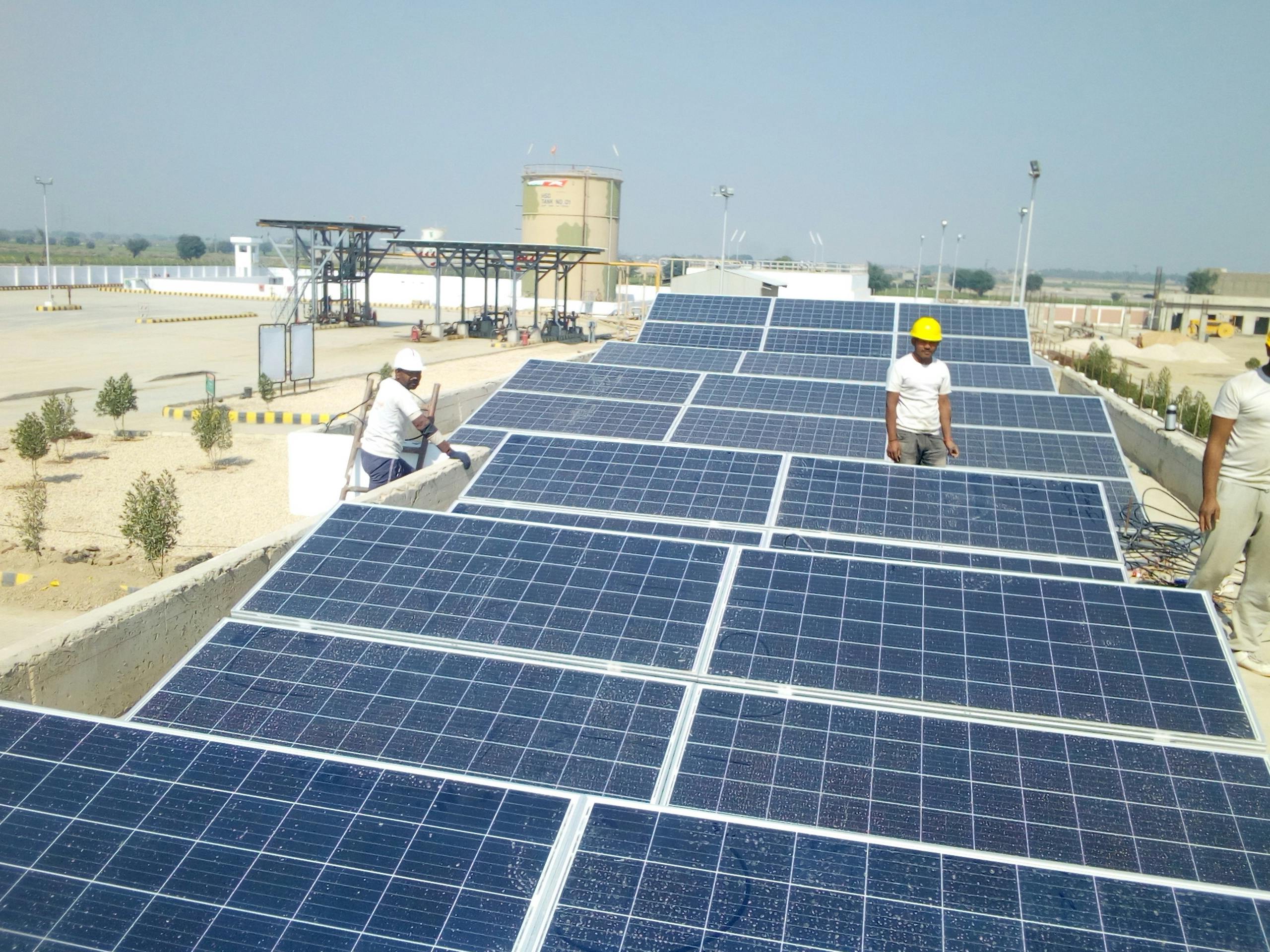
2. Rooftop Solar Program: Bringing Energy to Homes and Businesses
The Rooftop Solar Program is another cornerstone of India’s strategy to promote distributed energy. Advantages of the Rooftop Solar Program include:
- Enabling companies and residences to produce their electricity.
- Reducing the pressure on centralized grids.
- Promoting the use of clean, renewable energy in urban areas.
With a goal to achieve 40 GW of rooftop solar capacity, this program is pivotal in increasing the share of energy in distributed energy system in India.
3. Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPO): Encouraging Utility Investments
The Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO) is a regulatory framework that mandates electricity distribution companies to procure a certain percentage of their power from renewable sources. This policy plays a vital role in:
- Driving the adoption of distributed energy across India’s electricity grid.
- Encouraging utilities to invest in small-scale, decentralized energy projects.
- Integrating more renewable energy into the national grid to support sustainability.
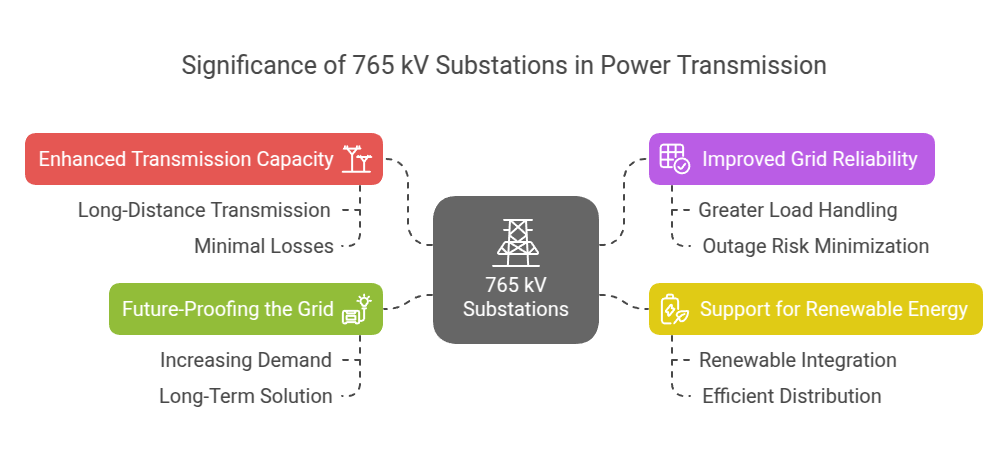
Technological Innovation in Grid Distribution Systems
The successful integration of distributed energy systems into India’s existing power grid requires advanced technology.
Benefits of Smart Grids:
- Smart grids provide real-time data, enabling utilities to monitor energy consumption and supply.
- They allow for better integration by managing the intermittent nature of renewable energy generation.
- These grids improve electric power distribution, ensuring a reliable and efficient energy supply.
Financing and Investment in Distributed Energy Systems
The Indian government, alongside private sector players and international investors, has committed to funding distributed energy projects across the country.
- The government offers subsidies for rooftop solar installations and small-scale solar power projects.
- Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are being increasingly leveraged to fund large-scale renewable energy projects.
- International investors, such as the World Bank and Asian Development Bank (ADB), are funding renewable energy initiatives in India.
Hartek Group: Transforming Distributed Energy in India
As one of India’s leading Engineering, Procurement and Construction companies in the energy sector, Hartek Group plays a vital role in driving the adoption of distributed energy systems.
Key Contributions:
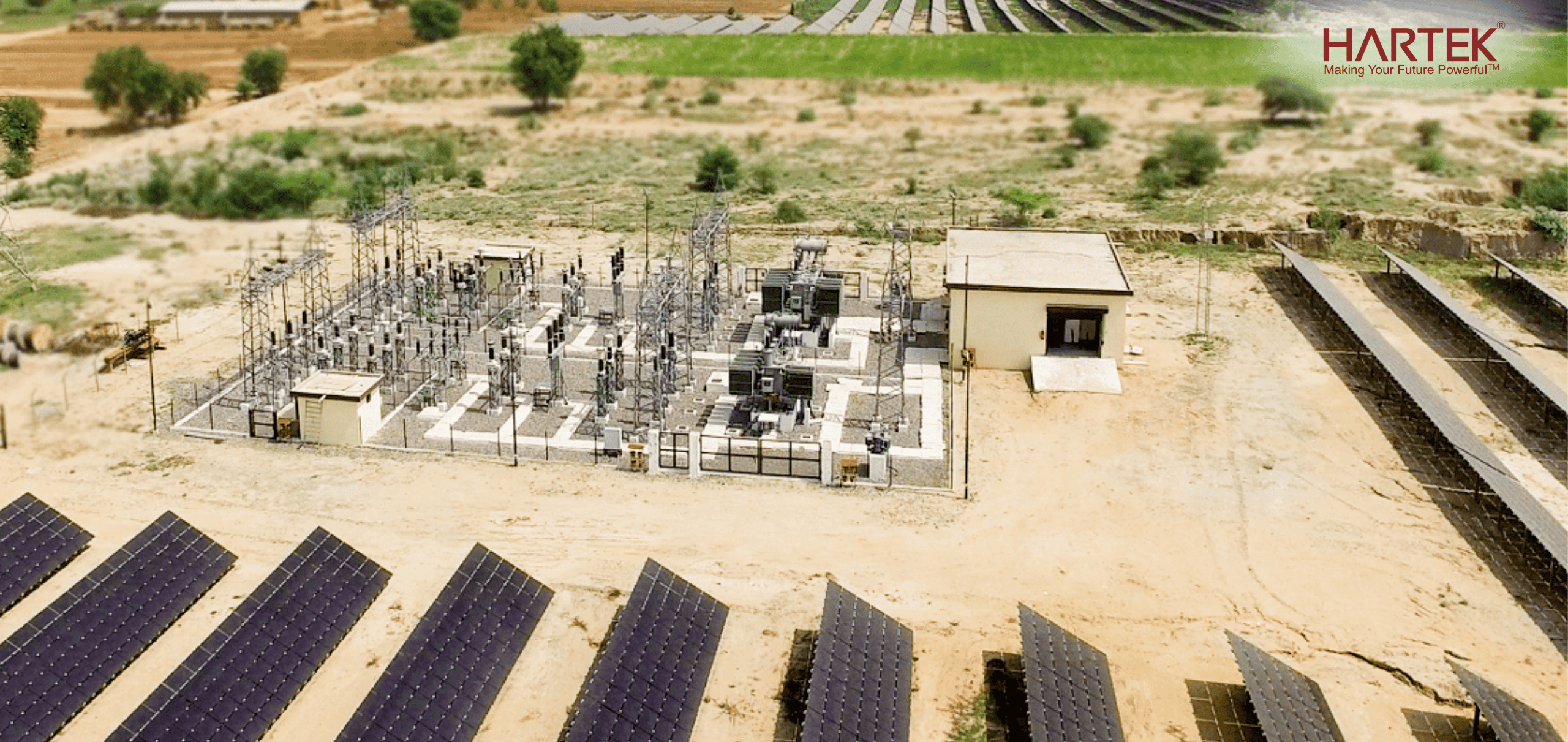
- Solar Solutions: Hartek has installed over 120 MW of solar rooftop capacity throughout India, empowering businesses and households with clean energy.
- Grid Modernization: The company isupgrading India’s grid distribution system with state-of-the-art substations, ensuring grid stability and supporting renewable energy integration.
- Smart Cities: Hartek actively supports India’s smart city initiatives by integrating renewable energy into urban power grids.
Commitment to Sustainability:
- Hartek Group focuses on delivering end-to-end solutions, from project design to execution, ensuring efficiency and reliability.
- Their expertise in renewable energy substations ensures seamless integration with India’s expanding renewable capacity.
With such contributions, Hartek is not just a company; it’s a driving force for change in India’s energy landscape.
Conclusion
India’s commitment to a clean, decentralized energy future is evident in the national policies that are driving the widespread adoption of distributed energy systems. Programs like PM-KUSUM, Rooftop Solar Yojana, and RPO are not just encouraging the adoption of renewable energy but are also fostering innovation in grid distribution and power management.
With continued policy support and technological advancements, companies like HARTEK ensure that the distribution energy system in India is set to lead the way, setting an example for the rest of the world to follow.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What is distributed energy, and why is it important for India?
Distributed energy refers to locally produced power from sources like solar and wind. It improves grid resilience, reduces transmission losses, and supports sustainability. -
How does the PM-KUSUM scheme promote distributed energy?
PM-KUSUM supports farmers with solar power solutions, reduces fossil fuel dependency for irrigation, and decentralizes electricity distribution in rural areas. -
What role does the Rooftop Solar Program play in India’s energy sector?
The program allows homes and businesses to generate their own electricity, easing the load on centralized grids and increasing India’s renewable energy share. -
How do smart grids support this energy systems?
Smart grids enable real-time energy monitoring, improve power distribution efficiency, and help integrate decentralized renewable energy into the main grid. -
How is Hartek Group contributing to India’s energy growth?
Hartek Group develops solar solutions, modernizes grid distribution, and integrates renewable energy into India’s smart cities, ensuring a sustainable energy future.