Solar energy is one of the cleanest sources of energy available in abundance, as per the department of energy. Despite the facts of its easy procurement and accessibility, there are some challenges faced by many developing countries like India.
Reports by the Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited (IREDA) reveal that solar energy can lower the power generation from fossil fuels in India if harnessed efficiently. In this blog, we will disclose the challenges rooftop solar panel manufacturers in India face after getting plenty of incentives. Besides the incentives offered by union and state governments, the growth of the SPV rooftop sector is beset with numerous obstacles. Among them are outlined in the subsequent section.
Challenges Faced While Implementing Rooftop Solar in India
Several challenges are present during the implementation of the solar rooftops. A few are outlined below-
1. The expensive initial outlay is required for installing solar panels on rooftops despite a roughly 50% worldwide drop in PV module prices since 2011. This price is considered expensive for a rooftop Solar Company In India too. As a result, costs continue to be higher for many customers.
2. The price of assembly components for power storage, such as batteries and inverters.
3. The grid’s stability is threatened by power from several modest solar installations. Grid integration challenges, including the possibility of power flow reversals across the network and unpredictable low voltage protection system.
4. Restrictions on the Feed in Tariff (FiT) strategy because of problems with monitoring and verification to prevent system abuse from feeding fuels that are subsidised.
5. Lack of awareness in consumers: Many people are still unaware about the schemes and other benefits provided by the government.
6. Technical specifications, such as voltage, flicker, and synchronization, need to be improved for the net-metering system.
7. Flip-Flopping Policies: Some states need to be more consistent regarding solar energy, creating uncertainty making it difficult for consumers and power distribution companies to make decisions.
8. Increased Taxes: Recently, taxes on different components of solar systems have been raised, which adds to the overall cost of adopting solar energy. This tax increase will impact the capital cost of solar systems by around 4-5%.
However, to solve these challenges, many steps have been taken by the government of India through some policies and schemes. Some of them are-
Solutions to Solve Hurdles in Rooftop Solar Implementation
1. The government has made a number of policy announcements to support solar energy. Imports are eligible for direct and indirect tax benefits, such as sales tax, excise duty exemptions, and custom duty exceptions.
2. In addition to accelerated depreciation (AD), which allows solar energy project developers to claim 80% of the expenditures in the first year itself, project developers were granted an exemption from income tax on all earnings from the project throughout its first ten years of operation.
3. To combat climate change, the government of India has announced mission-mode action plans for sustainable growth under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC). Its primary goal was to accelerate the development of solar energy. Additionally, it recommended raising RPOs to 5% of the entire cost of grid purchases.
4. Solar Energy Generation-Based Incentives (GBI): GBIs were introduced 2009 for small grid solar projects under 33 kV. They were introduced as a fiscal incentive to bridge the difference between the rate set by the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission and the base tariff of INR 5.5.
5. Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission: 2022 aimed to generate 20,000 MW of solar power capacity, of which 2,000 MW would come from off-grid sources.
6. Joint Liability Group (JLG) for Off-grid Installations: A small group of four to ten local entrepreneurs formed the JLG to combine their business and social potential to get loans for non-farming activities, including the application for micro-grid installations.
7. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): The top 500 corporations allocate 2% of their profits to off-grid solutions to satisfy social goals like pollution-free generating and to encourage the private sector’s participation in the country’s progress. This step will enhance the image of the company in front of stakeholders and guide others also to move towards sustainability.
Apart from these policies, many Government Schemes have also been introduced-
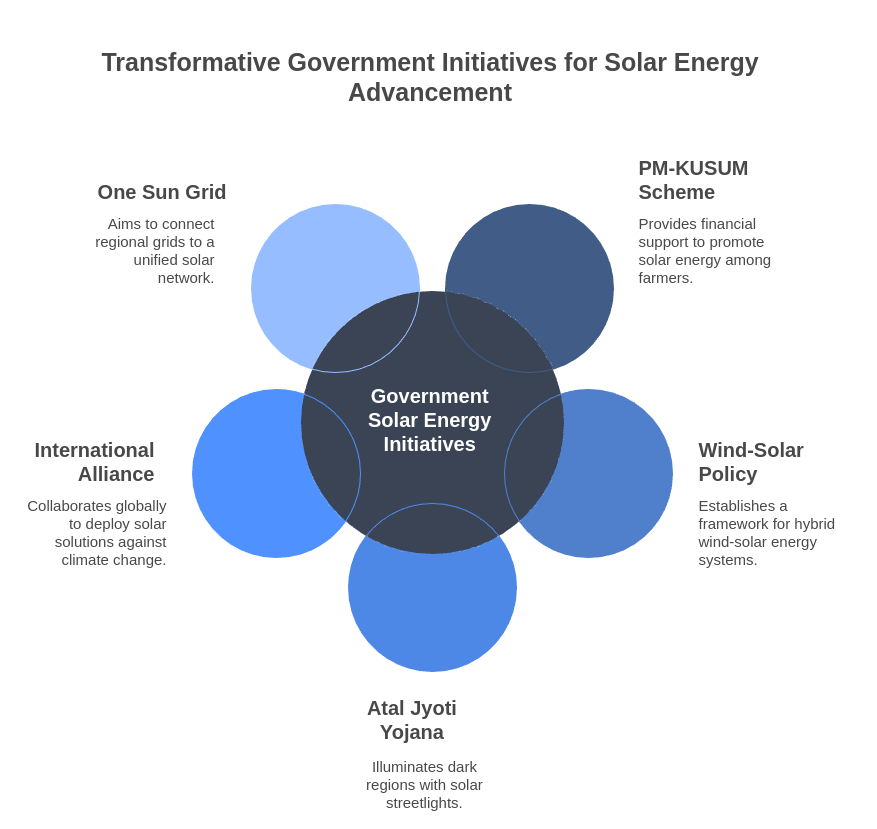
Schemes for Promoting Solar Energy
1. Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM) – Through this scheme central government will aid Rs. 34,422 Crore as financial support. The scheme is divided into 3 components and must be completed by 2026.
2. National wind-solar hybrid policy- In this scheme a framework will be provided for the promotion of large grid connected wind-solar PV hybrid system.
3. Atal Jyoti Yojana- Through this scheme dark regions of India will be illuminated with solar streetlights.
4. International Solar Alliance- It is a joint initiative of India and France to deploy the solar energy solutions against climate change.
5. One Sun, One World, One Grid- It is aimed to connect different regional grids to a common grid.
Conclusion
India is currently ranking fifth in the world for the distribution of solar power, and in the last five years, its utilisation has increased by more than 11 times.
Solar power has a lot to promise. As a result, the use of this renewable energy source will become necessary rather than just necessary, particularly in developing nations with high power demand like India. Therefore, challenges must be conquered with all the awareness and R&D required in this field. The R&D part can be fulfilled by including the private sector. An eminent Rooftop Solar Company In India like Hartek group can help in overcoming these above hurdles.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are the main challenges in rooftop solar adoption in India?
High initial costs, grid stability issues, lack of awareness, policy uncertainties, and increased taxes are key challenges faced in rooftop solar adoption. -
How is the government supporting rooftop solar power?
The government offers tax exemptions, subsidies, accelerated depreciation, and incentives like the PM-KUSUM scheme to promote solar adoption. -
What is the impact of taxes on rooftop solar installations?
Recent tax hikes on solar components have increased the cost of installation by 4-5%, making solar adoption more expensive for consumers. -
What are some key policies promoting solar energy in India?
Policies like the National Solar Mission, Atal Jyoti Yojana, and International Solar Alliance aim to expand solar energy and improve grid integration. -
How can private companies help in overcoming solar challenges?
Private firms like Hartek Group contribute through R&D, efficient installations, and maintenance services, ensuring better rooftop solar adoption.