Climate change looms large, and energy plays a central role in mitigating its devastating consequences. As global efforts focus on cutting greenhouse gas emissions, a comprehensive blueprint to transition the energy sector towards net-zero emissions by 2050 becomes vitally important; “Achieve Net Zero Emissions by 2050: An Energy Sector Blueprint” offers this necessary roadmap. This blueprint provides strategies for decarbonising energy production, increasing efficiency, and increasing the adoption of renewable sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal power. Now is the time to act; and here is how to achieve Net Zero Blueprint for 2050 as an ambitious yet necessary goal.
Ways to achieve India’s net zero target 2050
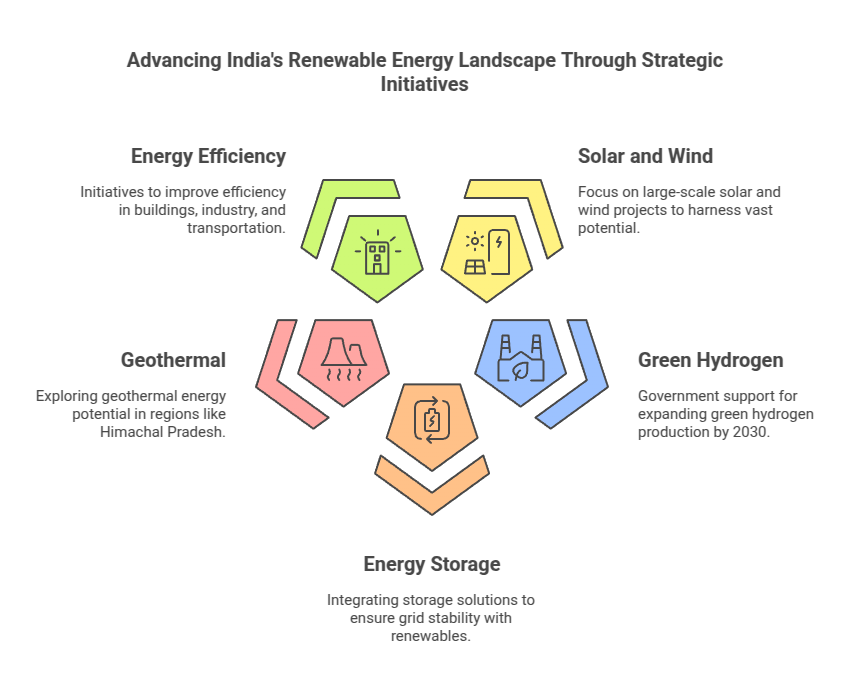
Renewable Energy Revolution
Renewable energy sources are at the core of any zero-net energy world, and here is how we can hasten their dominance:
- Solar Energy Explosion: Solar power holds immense promise due to its abundance and lower costs, making rooftop installations on homes and businesses, as well as large-scale solar farms, essential.
- Wind Power Expansion: Wind energy is an abundant and sustainable resource that should be utilized. By investing in both onshore and offshore wind farms, clean electricity production can increase substantially.
- Exploit Geothermal and Hydropower Energies: Harnessing geothermal energy from Earth’s core and expanding hydropower capacity at suitable locations can further diversify and strengthen the renewable energy mix.
- Emerging Renewables: Investigating and developing promising emerging renewable technologies like ocean energy (wave/tidal power) and concentrated solar power (CSP) could provide new options for clean energy solutions.
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind can produce intermittent power, meaning their production fluctuates depending on weather conditions. Energy storage solutions are therefore essential to ensure reliable and sustainable energy supplies:
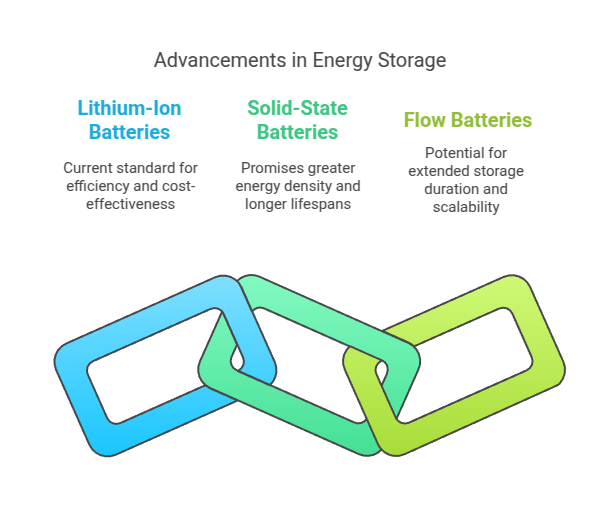
Battery Breakthroughs
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind offer exciting potential for a cleaner future, yet their intermittent nature presents challenges: How do we store this clean energy when needed most? That is where developments in battery technology, particularly Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), are making an incredible difference.
BESS: The Grid’s New Best Friend
BESS are large rechargeable batteries. At times of peak renewable energy production, excess solar or wind power is stored away to charge BESS batteries; when demand peaks or renewable resources become unavailable, this energy can then be released back into the grid, providing reliable power supply while optimizing utilization and decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. This integration is key to optimizing renewables’ utilization while simultaneously decreasing dependence.
Beyond BESS: A Multi-Pronged Approach
India’s clean energy strategy goes well beyond BESS; here are other key approaches:
- Pumped Hydro Power Gains Momentum: Pumped hydro power remains an invaluable technology. Excess energy is used to pump water uphill and store it in reservoirs before being released at peak demand to generate electricity using turbines.
- Exploring the Future of Storage: Innovations like compressed air energy storage (CAES) and hydrogen storage hold great promise for long-term energy storage requirements.
- Demand-Side Management: A Two-Way Street: Optimizing energy usage through efficiency measures is key to increasing clean energy supply.
- Retrofitting for Efficiency: Retrofitting existing buildings with improved insulation, energy-saving windows and energy efficient appliances can dramatically lower their energy footprint. Implementing stringent building codes on new builds will further boost overall energy efficiency.
India is taking an integrative approach to renewable energy integration. BESS serves as an integral component of this effort and ensures a future powered by clean, reliable, and sustainable sources of power.
India’s Clean Energy Hustle: A Ground-Up Movement
Integrating intelligent smart grid technologies with two-way communications enables dynamic pricing models that encourage energy use during off-peak hours and optimize grid operations.
- Smart Grids for Smarter Living: Imagine a power grid that responds! India’s smart grid initiatives use two-way communication to enable dynamic pricing models and allow for dynamic electricity pricing at off-peak hours – incentivizing people to reduce energy use while relieving strain on the overall grid infrastructure.
- Empowering Every Watt: Shifting mindsets is at the core of India’s clean energy mission. Public awareness campaigns aim to educate citizens on simple yet impactful actions they can take – such as remembering to turn off lights when leaving a room and choosing energy efficient appliances; smart thermostats; etc – that will allow everyone in India to become energy savers.
- Clean Rides for a Greener Future: India is taking direct steps to address emissions from transportation by spearheading an initiative for clean mobility: India has initiated an impressive clean mobility revolution:
- E-Vehicle Explosion: Electric Vehicles (EVs) have come to the forefront, as government leaders push for mass adoption across vehicles from personal cars to public buses and even commercial trucks. This involves creating an effective charging infrastructure network and offering purchase incentives; all while encouraging the creation of affordable electric models.
- Public Transport Makeover in India: India has invested significantly in improving its public transportation system. Efficient bus, train, and subway networks are being created that connect seamlessly to cycling and pedestrian infrastructure – this focus on public transportation is designed to reduce dependence on private vehicles significantly.
- Clean Fuels to Meet Specific Needs: For heavy-duty vehicles such as long-haul trucks and airplanes, immediate electrification might not be practical. India is exploring alternative clean fuel sources – hydrogen from renewable energy sources could be one promising choice, while biofuels must also be carefully evaluated for their environmental impacts.
India’s clean energy policy combines innovation and social change. By emphasizing smart technologies as well as behavioral shifts, India is creating a sustainable energy future for its citizens.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)
CCUS technologies capture CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial facilities before they escape into the atmosphere and convert them to valuable products or uses such as:
- Underground Storage of CO2: Geologic formations offer safe and secure CO2 storage that won’t release it back into the atmosphere.
- Captured CO2 Can Be Utilized in Industrial Processes: Captured CO2 can be put to good use in various industrial processes, including enhanced oil recovery (EOR). EOR is used to increase oil production while simultaneously storing CO2 underground; however, this approach must be monitored closely so as not to increase emissions elsewhere.
- Nature-Based Solutions: Although much focus has been placed on mitigating emissions at their source, natural ecosystems also play a vital role in carbon sequestration and should be harnessed towards reaching net zero carbon dioxide emissions.
- Forest Restoration and Conservation: Protecting existing forests while revitalizing degraded ones is an effective way to increase carbon storage capacity, so sustainable forestry practices that promote healthy forests are essential.
- Blue Carbon Initiatives: Preserving and restoring coastal ecosystems such as mangroves and seagrass meadows can significantly increase carbon neutrality from the atmosphere.
In the Nutshell
Going green by 2050 may seem an ambitious goal, but with our united efforts, we can do it! Countries, businesses, and individuals all play a role. Think of it as a team effort: by investing in cleaner methods of energy generation and development while learning smarter use practices, we can achieve a future where all energy sources are clean. Together, this plan serves as our game plan in our battle against climate change—let’s do this together.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is clean energy, and why is it important?
Clean energy comes from renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydro, reducing carbon emissions and mitigating climate change. -
How can India achieve net-zero emissions by 2050?
By expanding renewable energy, improving energy storage, adopting smart grids, promoting electric mobility, and investing in carbon capture technologies. -
What role do energy storage solutions play in clean energy?
Energy storage systems like batteries and pumped hydro store excess renewable energy, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply. -
How can individuals contribute to clean energy adoption?
By using energy-efficient appliances, supporting renewable energy, reducing waste, and adopting electric vehicles or public transport. -
What is carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS)?
CCUS captures CO₂ emissions from industries and stores them underground or repurposes them for industrial applications, reducing atmospheric emissions.